Stigma Of Pathological Gambling Disorders
Stigma toward problem gambling can reduce the chance that people will seek help, including professional treatment. Gambling and Stigma. While many people view gambling as a socially acceptable way to have fun, there is a certain level of social stigma attached to it. For some, gambling itself is suspect. When it comes to people who are perceived as ‘problem gamblers,' the stigma is even stronger. Public attitudes include negative stereotypes about people.
Gambling and Mental Health
Instructor: Dr. Dawn-Elise Snipes
Executive Director: AllCEUs.com Counselor Education & Training

- Stigma has been identified as a major barrier to help-seeking, treatment and recovery from gambling problems. However, little research has attempted to examine in any depth the causes.
- Pathological gambling (Westermeyer et al., 2013). A national survey of U.S. Veterans found that approximately 2.2% screened positive for at-risk or pathological gambling (Stefanovics, Potenza, & Pietrzak, 2017). 4.2% of Iraq/Afghanistan Veterans exhibit at -risk or probable disordered gambling (Whiting et al., 2016).
CEUs/OPD/CPDs are available for this presentation at https://www.allceus.com/member/cart/index/product/id/664/c/ for clinicians in the US and https://australia.allceus.com/member/cart/index/product/id/664/c/ for clinicians in Australia.

First Responsible Gaming Program
Objectives
~ Post-traumatic stress symptoms in pathological gambling: Potential evidence of anti-reward processes
~ Problem gambling in bipolar disorder
~ Alexthymia and Pathological Gambling
~ Food addiction in gambling disorder
~ Gambling, domestic violence and trauma
~ Understanding stigma
Post Traumatic Stress and Gambling
~ When the number of traumatic events were controlled for, individuals with pathological gambling disorder had significantly higher PTS scores
~ 'Anti-reward' gambling provides momentary relief from PTS but contributes to the 'spiraling distress cycle'
~ In a study of pathological gamblers, gambling behavior significantly decreased upon completion of PTSD treatment (Najavits et al., 2013)
~ People with a history of trauma should be counseled about their increased risk for developing gambling problems
Bipolar Disorder
~ People who met criteria for Bipolar 1 (full manic) and pathological gambling were identified
~ The general population had a 3.8% prevalence of problem gambling
~ The group with bipolar disorder had a 11.6% prevalence of problem gambling
~ Of all psychiatric categories examined, respondents screening positive for a manic episode had the highest risk of pathological gambling
~ Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors may be effective for some patients with pathological gambling
Bipolar Disorder
~ Sustained release lithium appears to produce significant positive results in gambling behaviors and affective stability after 8 to 10 weeks as measured by the
~ Clinical Global Impression (CGI) pathological gambling improvement scale
~ Clinician-Administered Rating Scale for Mania
Alexthymia
~ Individuals with high levels of alexithymia become prone to addictive behavior via emotional dysregulation
~ Alexithymia
~ difficulty in describing feelings
~ distinguishing one's feelings from bodily sensations
~ having restricted imaginative processes
~ a stimulus-dependent, externally oriented cognitive style
~ challenges in emotional processing and coping with stressful feelings/ emotional regulation
~ Alexithymic individuals
~ attempt to regulate their emotions through compulsive behaviors.
~ show addictive behaviors due to their lack of self-knowledge and insight.
Alexthymia
~ Emotional dysregulation was measured using the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale (DERS)
~ Difficulties in emotion regulation and alexithymia are positive, significant predictors of pathological gambling
Gambling and Domestic Violence
~ 25-50% of spouses of compulsive gamblers have been abused
~ Odds ratio of intimate partner violence increased 10.5 times when partner was problem gambler
~ Children of problem gamblers are 2 to 3 times more likely to be abused by a parent
~ For many women gambling venues are refuge from violence and gambling becomes a method of escape
~ Family violence and addiction have several common features including loss of control, continuation despite adverse consequences, tolerance and withdrawal, involvement of the entire family, preoccupation or obsession and defenses of denial, minimization and rationalization
Gambling and Trauma
~ In a twin cohort study, experiencing traumatic events increases the risk of having a gambling problem by up to 453%
~ Problem gamblers are 620% more likely to develop PTSD
~ Soldiers who are returning from deployment tend to have a greater propensity for risk taking and often have experienced trauma putting them at greater risk for the development of PG
Food Addiction in Gambling Disorder
~ Recent research supports the notion that food may have addictive potential in some individuals due to the increased potency of certain nutrients, palatability, or natural reward (i.e. dopamine and serotonin)
~ Palatable foods can mimic the neurophysiological and behavioral effects of addictive drugs
~ Systematic reviews confirm commonalties between GD and other behavioral addictions (including FA)
~ Impulsivity and compulsivity
~ Structural and functional abnormalities of networks involved in reward processing and top-down control
~ Alterations in neurochemical-neuroendocrine systems
~ Increased negative urgency, disinhibition and novelty seeking
~ Familial diathesis (history)
Food Addiction in Gambling Disorder
~ Distinct subtypes of GD patients described the as 'disorganized and emotionally unstable'
~ The co-occurrence of FA in treatment-seeking GD patients is related to poorer emotional and psychological states
~ Higher ratio of FA was found in women
~ There was a higher risk of a FA diagnosis in patients with
~ High scores for
~ Harm avoidance (escape)
~ Self-transcendence: Unconventional, illogical, suspicious, and immature
~ Low scores in cooperativeness
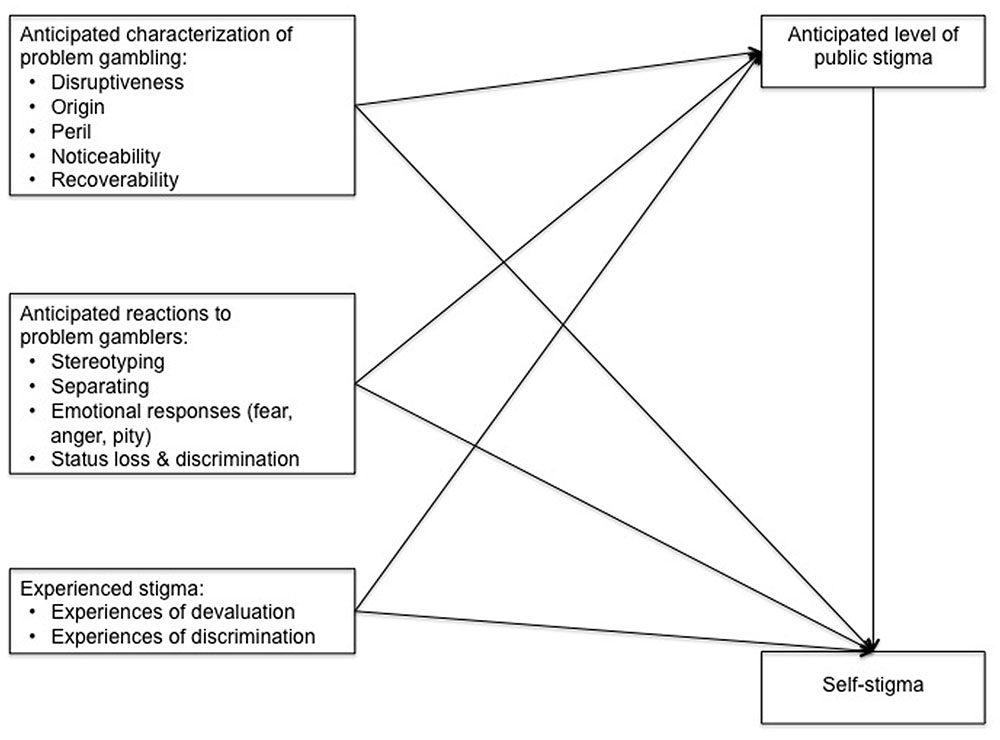
Stigma
~ As a result of stigma, people with gambling problems attracted substantial negative stereotypes, social distancing, emotional reactions, and status loss/discrimination
~ Stigmatizing attitudes held toward people experiencing problem gambling
~ Impulsive
~ Irrational
~ Irresponsible
~ Untrustworthy
~ Unproductive
~ Greedy
~ Antisocial
Stigma
~ Stereotypes of 'problem gamblers' are socially constructed from transmitted cultural beliefs rather than cognitively derived from direct interactions.
~ Culturally constructed stereotypes are more resistant to contradictory evidence and education campaigns, but increased contact with the stigmatized population appears to reduce stigma
~ Desired social distance increased with perceptions that problem gambling is caused by bad character, is perilous, non recoverable and disruptive, but decreased with perceptions that it is due to stressful life circumstances or a chemical brain imbalance
~ Individuals experiencing gambling problems have expressed aversion to being pitied, wanting instead to be treated like everybody else
Summary
~ Anti-reward processes, or the immediate, short term escape followed by worsening of the condition is very common in people with PTS.
~ People with pathological gambling disorder have higher PTS scores
~ Gambling is a high-risk behavior that people with bipolar disorder may undertake to escape depressive mood states or for excitement during manic states
~ Time-released lithium was found to improve gambling urges as well as emotional lability
~ People with alexthymia have difficulty identifying and therefore regulating their emotions. Gambling can provide an escape/numbing of unpleasant physiological or emotional states.
- Stigma has been identified as a major barrier to help-seeking, treatment and recovery from gambling problems. However, little research has attempted to examine in any depth the causes.
- Pathological gambling (Westermeyer et al., 2013). A national survey of U.S. Veterans found that approximately 2.2% screened positive for at-risk or pathological gambling (Stefanovics, Potenza, & Pietrzak, 2017). 4.2% of Iraq/Afghanistan Veterans exhibit at -risk or probable disordered gambling (Whiting et al., 2016).
CEUs/OPD/CPDs are available for this presentation at https://www.allceus.com/member/cart/index/product/id/664/c/ for clinicians in the US and https://australia.allceus.com/member/cart/index/product/id/664/c/ for clinicians in Australia.
First Responsible Gaming Program
Objectives
~ Post-traumatic stress symptoms in pathological gambling: Potential evidence of anti-reward processes
~ Problem gambling in bipolar disorder
~ Alexthymia and Pathological Gambling
~ Food addiction in gambling disorder
~ Gambling, domestic violence and trauma
~ Understanding stigma
Post Traumatic Stress and Gambling
~ When the number of traumatic events were controlled for, individuals with pathological gambling disorder had significantly higher PTS scores
~ 'Anti-reward' gambling provides momentary relief from PTS but contributes to the 'spiraling distress cycle'
~ In a study of pathological gamblers, gambling behavior significantly decreased upon completion of PTSD treatment (Najavits et al., 2013)
~ People with a history of trauma should be counseled about their increased risk for developing gambling problems
Bipolar Disorder
~ People who met criteria for Bipolar 1 (full manic) and pathological gambling were identified
~ The general population had a 3.8% prevalence of problem gambling
~ The group with bipolar disorder had a 11.6% prevalence of problem gambling
~ Of all psychiatric categories examined, respondents screening positive for a manic episode had the highest risk of pathological gambling
~ Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors may be effective for some patients with pathological gambling
Bipolar Disorder
~ Sustained release lithium appears to produce significant positive results in gambling behaviors and affective stability after 8 to 10 weeks as measured by the
~ Clinical Global Impression (CGI) pathological gambling improvement scale
~ Clinician-Administered Rating Scale for Mania
Alexthymia
~ Individuals with high levels of alexithymia become prone to addictive behavior via emotional dysregulation
~ Alexithymia
~ difficulty in describing feelings
~ distinguishing one's feelings from bodily sensations
~ having restricted imaginative processes
~ a stimulus-dependent, externally oriented cognitive style
~ challenges in emotional processing and coping with stressful feelings/ emotional regulation
~ Alexithymic individuals
~ attempt to regulate their emotions through compulsive behaviors.
~ show addictive behaviors due to their lack of self-knowledge and insight.
Alexthymia
~ Emotional dysregulation was measured using the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale (DERS)
~ Difficulties in emotion regulation and alexithymia are positive, significant predictors of pathological gambling
Gambling and Domestic Violence
~ 25-50% of spouses of compulsive gamblers have been abused
~ Odds ratio of intimate partner violence increased 10.5 times when partner was problem gambler
~ Children of problem gamblers are 2 to 3 times more likely to be abused by a parent
~ For many women gambling venues are refuge from violence and gambling becomes a method of escape
~ Family violence and addiction have several common features including loss of control, continuation despite adverse consequences, tolerance and withdrawal, involvement of the entire family, preoccupation or obsession and defenses of denial, minimization and rationalization
Gambling and Trauma
~ In a twin cohort study, experiencing traumatic events increases the risk of having a gambling problem by up to 453%
~ Problem gamblers are 620% more likely to develop PTSD
~ Soldiers who are returning from deployment tend to have a greater propensity for risk taking and often have experienced trauma putting them at greater risk for the development of PG
Food Addiction in Gambling Disorder
~ Recent research supports the notion that food may have addictive potential in some individuals due to the increased potency of certain nutrients, palatability, or natural reward (i.e. dopamine and serotonin)
~ Palatable foods can mimic the neurophysiological and behavioral effects of addictive drugs
~ Systematic reviews confirm commonalties between GD and other behavioral addictions (including FA)
~ Impulsivity and compulsivity
~ Structural and functional abnormalities of networks involved in reward processing and top-down control
~ Alterations in neurochemical-neuroendocrine systems
~ Increased negative urgency, disinhibition and novelty seeking
~ Familial diathesis (history)
Food Addiction in Gambling Disorder
~ Distinct subtypes of GD patients described the as 'disorganized and emotionally unstable'
~ The co-occurrence of FA in treatment-seeking GD patients is related to poorer emotional and psychological states
~ Higher ratio of FA was found in women
~ There was a higher risk of a FA diagnosis in patients with
~ High scores for
~ Harm avoidance (escape)
~ Self-transcendence: Unconventional, illogical, suspicious, and immature
~ Low scores in cooperativeness
Stigma
~ As a result of stigma, people with gambling problems attracted substantial negative stereotypes, social distancing, emotional reactions, and status loss/discrimination
~ Stigmatizing attitudes held toward people experiencing problem gambling
~ Impulsive
~ Irrational
~ Irresponsible
~ Untrustworthy
~ Unproductive
~ Greedy
~ Antisocial
Stigma
~ Stereotypes of 'problem gamblers' are socially constructed from transmitted cultural beliefs rather than cognitively derived from direct interactions.
~ Culturally constructed stereotypes are more resistant to contradictory evidence and education campaigns, but increased contact with the stigmatized population appears to reduce stigma
~ Desired social distance increased with perceptions that problem gambling is caused by bad character, is perilous, non recoverable and disruptive, but decreased with perceptions that it is due to stressful life circumstances or a chemical brain imbalance
~ Individuals experiencing gambling problems have expressed aversion to being pitied, wanting instead to be treated like everybody else
Summary
~ Anti-reward processes, or the immediate, short term escape followed by worsening of the condition is very common in people with PTS.
~ People with pathological gambling disorder have higher PTS scores
~ Gambling is a high-risk behavior that people with bipolar disorder may undertake to escape depressive mood states or for excitement during manic states
~ Time-released lithium was found to improve gambling urges as well as emotional lability
~ People with alexthymia have difficulty identifying and therefore regulating their emotions. Gambling can provide an escape/numbing of unpleasant physiological or emotional states.
Stigma Of Pathological Gambling Disorders
Summary
~ Similar to other addictions, there is a high correlation between food addiction and gambling disorder.
~ In families where someone has pathological gambling disorder, there are significantly higher rates of domestic violence and child abuse.
~ Stigma often causes people to refuse to seek help.
~ Stigma regarding gambling appears to be largely culturally created
~ Exposure to people who have pathological gambling disorder to reduce othering shows the greatest promise for the reduction of stigma.
